| Telephone Cables | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
 Foam Skin Insulated & LAP Sheathed Jelly Filled Cables to RUS(REA) PE-89
Foam Skin Insulated & LAP Sheathed Jelly Filled Cables to RUS(REA) PE-89
Application
The cables are designed for use in access or trunk networks, from telephone exchange to subscriber area. The
cables are suitable for installation in ducts, direct burial in the ground and also for aerial installation with integral
suspension strand. Jelly filled option is for subscriber’s cables installed underground or along the edge of
pavement. An armoured option is offered for direct burial installations where additional mechanical or rodent
protection is required. A figure-8 self support option is offered for aerial installation.
Standards
RUS(REA) PE-89 (RUS 7 CFR 1755.890)
Construction

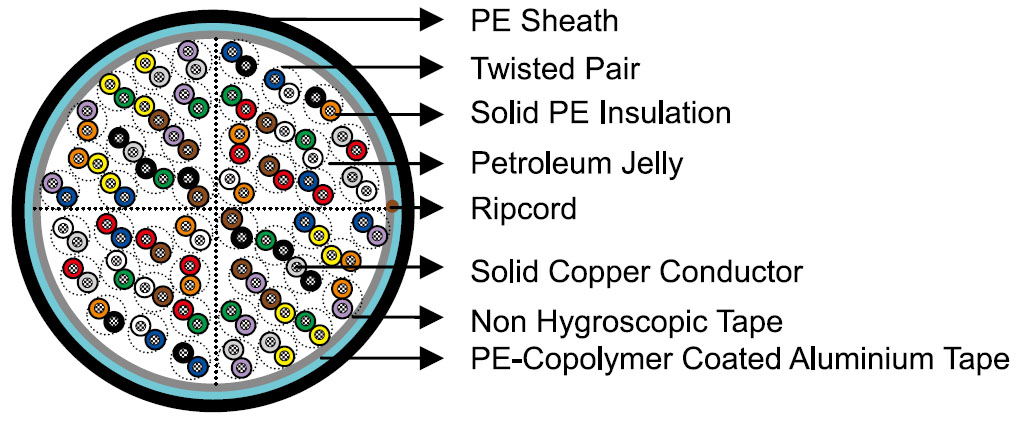
Conductors
Solid annealed bare copper, 0.4/0.5/0.63/0.9mm as per ASTM B-3/class1 of IEC 60028
Insulation
Foam Skin which is a composite polyethylene insulation made of an inner cellular layer and an outer solid skin as
per ASTM D 1248/IEC 60708
Twisted Pairs
Insulated conductors are twisted into pairs with varying lay length to minimize crosstalk
CablingElement
Twisted Pairs
Cable Core Assembly
Cables of 25 pairs or less are assembled into cylindrical core. Cables larger than 25 pairs are assembled into
units, which are then used to form the core Units are identified by colour coded binders. Standard construction is
per RUS(REA) PE-89 given in Cable Make Up Diagram
Core Wrapping
One or more non-hygroscopic polyester tapes are helically or longitudinally laid with an overlap. These tapes
furnish thermal, mechanical as well as high dielectric protection between shielding and individual conductors
Moisture Barrier
A corrugated copolymer coated aluminium tape (0.2mm/8mil) is applied directly over the cable core to provide
100% electrical shielding coverage and ensure a barrier against water vapor
Filling
The cable core interstices are filled with petroleum jelly to avoid longitudinal water penetration within the
cable.The water resistant filling compound is applied to the air space between non-hygroscopic tape and shield,
shield and sheath within the cable core
Sheath
Black low density polyethylene as per ASTM D 1248/IEC 60708, being able to withstand exposure to
sunlight,temperature variations, ground chemicals and other environmental contaminants
Ripcord(optional)
Ripcord may be provided for slitting the sheath longitudinally to facilitate its removal
Spare Pairs (optional)
Spare pairs may be incorporated for large pair cables
Continuity Wire (optional)
One tinned copper drain wire may be longitudinally laid to ensure electrical continuity of the screen

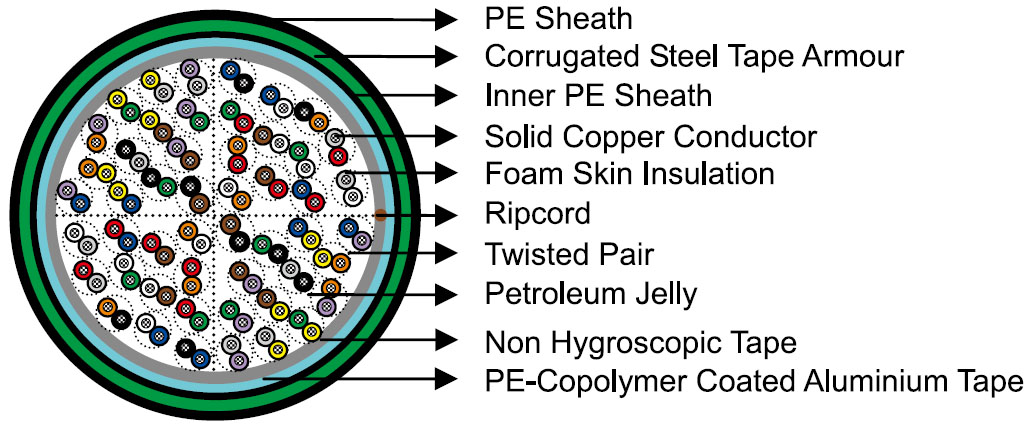
Optional Construction
Armoured Cable
Corrugated copolymer coated steel tape armour (0.15mm/6mil) is applied with an overlap over an optional inner polyethylene sheath. An outer polyethylene sheath is applied over the armour
Self-Support Cables
A 7-strand galvanized steel strand is used as support wire. Black polyethylene sheath covers both core and support wire in a figure-8 construction
Electrical Properties
| Nominal Conductor Diameter | mm | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.63 | 0.9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductor Gauge Size | AWG | 26 | 24 | 22 | 19 |
| Maximum Average DC Resistance | Ω/km / Ω/mile | 140/225 | 87/140 | 55/88.6 | 27.0/43.4 |
| Maximum Individual DC Resistance | Ω/km / Ω/mile | 144.2/232 | 89.5/144 | 56.5/91.0 | 28.0/45.0 |
| Minimum Insulation Resistance @500V DC | MΩ.km / MΩ.mile | 1600/1000 | 1600/1000 | 1600/1000 | 1600/1000 |
| Maximum Average Resistance Unbalance | % | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Maximum Individual Resistance Unbalance | % | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Average Mutual Capacitance | nF/km / nF/kft | 48.5-54.0 /14.8-16.5 |
48.5-54.0 /14.8-16.5 |
48.5-54.0 /14.8-16.5 |
48.5-54.0 /14.8-16.5 |
| Maximum Individual Mutual Capacitance | nF/km / nF/kft | 57/17.4 | 57/17.4 | 57/17.4 | 57/17.4 |
| Maximum Individual Capacitance Unbalance pair-to-pair | pF/km / pF/kft | 145/44 | 145/44 | 145/44 | 145/44 |
| Capacitance Unbalance RMS pair-to-pair | pF/km / pF/kft | 45/13.7 | 45/13.7 | 45/13.7 | 45/13.7 |
| Maximum Individual Capacitance Unbalance pair-to-ground |
pF/km / pF/kft | 2625/800 | 2625/800 | 2625/800 | 2625/800 |
| Maximum Average Capacitance Unbalance pair-to-ground | pF/km / pF/kft | 574/175 | 574/175 | 574/175 | 574/175 |
| Maximum Conductor Loop Resistance @20°C | Ω/km / Ω/mile | 300/482 | 192/309 | 114/183.6 | 60/96.4 |
| Impedance @1KHz | Ω | 994 | 796 | 660 | 445 |
| Impedance @100KHz | Ω | 147 | 134 | 125 | 122 |
| Impedance @512KHz | Ω | 120 | 118 | 117 | 116 |
| Impedance@1MHz | Ω | 117 | 115 | 114 | 113 |
| Maximum Average Attenuation @0.8KHz | dB/km / dB/kft | 1.64/0.5 | 1.30/0.39 | 1.04/0.32 | 0.74/0.22 |
| Maximum Average Attenuation@1KHz | dB/km / dB/kft | 1.68/0.51 | 1.35/0.41 | 1.08/0.33 | 0.76/0.23 |
| Maximum Average Attenuation @3KHz | dB/km / dB/kft | 3.18/0.97 | 2.52/0.77 | 2.01/0.61 | 1.42/0.43 |
| Maximum Average Attenuation @150KHz | dB/km / dB/kft | 11.4/3.47 | 8.3/2.53 | 6.2/1.89 | 4.4/1.34 |
| Maximum Average Attenuation @772KHz | dB/km / dB/kft | 24.3/7.4 | 19.4/5.9 | 15.4/4.7 | 10.8/3.3 |
| Maximum Average Attenuation @1000KHz | dB/km / dB/kft | 27.1/8.25 | 21.4/6.52 | 17.5/5.33 | 12.8/3.89 |
| Dielectric Strength | |||||
| Conductor to Conductor (3secs) | V DC | 2400 | 3000 | 4000 | 5000 |
| Conductor to Screen (3secs) | V DC | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 |
| Minimum EL Far-end Cross-talk-Mean Power Sum | |||||
| @150KHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 61 | 63 | 63 | 65 |
| @772KHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 47 | 49 | 49 | 57 |
| @1.6MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 |
| @3.15MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 35 | 37 | 37 | 39 |
| @6.3MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 29 | 31 | 31 | 33 |
| Minimum Far-end Cross-talk-Worst Pair Power Sum | |||||
| @150KHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 57 | 57 | 57 | 59 |
| @772KHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 43 | 43 | 43 | 45 |
| @1.6MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 37 | 37 | 37 | 39 |
| @3.15MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 31 | 31 | 31 | 33 |
| @6.3MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 25 | 25 | 25 | 27 |
| Minimum Near-end Cross-talk-Mean Power Sum | |||||
| @150KHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 58 | 58 | 58 | 58 |
| @772KHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 |
| @1.6MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 43 | 43 | 43 | 43 |
| @3.15MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 |
| @6.3MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 34 | 34 | 34 | 34 |
| Minimum Near-end Cross-talk-Worst Pair Power Sum | |||||
| @150KHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 53 | 53 | 53 | 53 |
| @772KHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 |
| @1.6MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 |
| @3.15MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 |
| @6.3MHz | dB/305m / dB/kft | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 |
| Nominal Insulation Thickness | mm | 0.175 | 0.2 | 0.26 | 0.3 |
| Nominal Insulated Conductor Diameter | mm | 0.75 | 0.9 | 1.15 | 1.5 |
1 2







